OVERVIEW
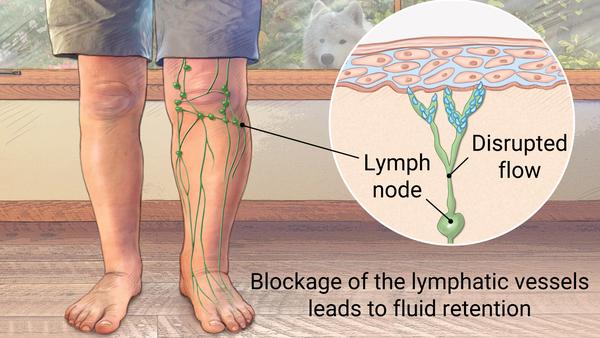
Lymph is a fluid that circulates around the body, carrying essential substances such as white blood cells, proteins, salts, fat, water, etc. Lymphoedema is swelling which affects the limbs due to failure of the vessels responsible for transporting the lymph. Lymphatic vessels serve to help drain fluid from the extremities as well as acting as an immune gatekeeper. Glands that filter lymph is known as lymph nodes.
SYMPTOMS
- Swelling in the arms and/or legs, particularly in fingers and toes
- Swelling in the head/neck
- A feeling of heaviness/aching
- Tightening of the skin
- Fatigue
- Fluid leakage through the skin
- Difficulty with basic movement
- More frequent infection
- Chronic wounds
CAUSES/RISK FACTORS
Primary lymphoedema is rare and often due to the absence of lymph from birth or the failure of the lymphatic system to work overtime. Patients can present with swollen limbs at birth (congenital absence of lymphatics) or in their teenage years (delayed primary failure).
Secondary lymphoedema is more common and is often the result of surgery to remove the lymph nodes (e.g. surgery for breast cancer and axilla lymph node clearance) or radiation therapy to the lymph nodes (e.g. radiation to the groin or pelvic lymph nodes). Sometimes recurrent skin infections (cellulitis) can also damage the lymphatic drainage of the limbs.
DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis requires:
- Obtaining a history of duration of limb swelling.
- Exclusion of other causes of limb swelling such as associated vein disease, muscle and soft tissue infections and injury.
- A lymphoscintigraphy (specialised scan) may be done to determine primary vs secondary lymphoedema as well as the extent of the disease.
OUR TREATMENTS
The main aim of treatment is to reduce the limb swelling and restore functionality.
- Lymphatic drainage massage as well as compression dressings help reduce swelling significantly, but both have to be done regularly (usually three times a week).
- Newer therapies include surgery to connect the blocked lymph drainage channels to small veins (lymphovenous bypass) or lymph node transplants to the affected limb.
References:
